Staging and Treatment
Staging & Treatment
- N Breast Cancer Staging
- NBreast Cancer staging is based on the following parameters
- NThe size of the lesion/lump/tumor
- NWhether the cancer is localized to the breast only
- NWhether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
- NWhether cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
TNM staging system.
- TNM staging system takes in to account.
- Tumour size (T stands for tumor)
- Lymph node involvement (N stands for node)
- Whether the cancer has metastasized (M stands formetastasis), or moved
- beyond the breast to other parts of the body.
Treatment is individualized based on these factors:.
- NClinical stage of breast cancer
- NHistopathologic grade of the tumor
- N Pre or Post Menopausal Status
- N Hormone Receptor Status.
- NPerformance Status/ General Health.
- NType of Breast Cancer Surgery
Types of Cancer Surgery
Lumpectomy: Tumor along with an area of normal tissue as margin is removed. Quadrantectomy: Quadrant(part of breast) involved by the tumor is removed. Simple mastectomy: Entire breast tissue (including the skin and nipple) is removed. Radical mastectomy: Entire breast tissue along with chest wall muscles are removed. Modified radical mastectomy: Entire breast tissue with axillary lymph nodes are removed sparing the chest wall muscles.Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer
Radiotherapy involves using ionizing radiation to destroy cancer cells. It is a common adjuvant treatment after surgery especially after breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) to the remaining breast tissue. Can be delivered as external beam radiation, delivered from machine to the target tissue or brachytherapy (radioactive seeds/pellets placed near cancer site)Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
A modality of treatment in which drugs are administered to kill cancer cells. Three scenarios where it is used: ADJUVANT THERAPY – Given after initial surgery and/or radiation; to prevent cancer from coming back. NEO-ADJUVANT THERAPY – Given before surgery to reduce the tumor size and possibly make the surgery easier. METASTATIC DISEASE – As maintenance therapy when cancer has spread to other parts of the body.Stage wise Treatment of Breast Cancer
The stage of the disease is an important determinant in choosing the treatment options. Factors that influence treatment options are:- NHORMONE RECEPTOR STATUS – ESTROGEN/PROGESTERONE.
- NHER2 protein AND KI 67 INDEX STATUS
- NPERFORMANCE STATUS AND PATIENT CHOICES
- NMENOPAUSAL STATUS
- NGRADE OF TUMOR
Stage 0
Disease limited to the lining of the milk ducts only; MEDICALLY LABELLED AS DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU (DCIS)
Considered as NON-INVASIVE.
LOBULAR CARCINOMA IN SITU IS NOT CONSIDERED AS CANCER BUT AS A HIGHER RISK PREDICTOR OF CANCER.
Stages I-III
Treatment includes Surgery and Radiotherapy; may or may not include chemotherapy or hormonal therapy.
Stages I.
Disease limited to the breast tissue with either no spread to lymph nodes or limited spread (Sentinel Node – First node to which cancer is likely to spread).Stages II.
Tumor larger than Stage I and has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stages III.
The large tumor has spread to surrounding tissues (Skin /Chest muscles) with many lymph nodes
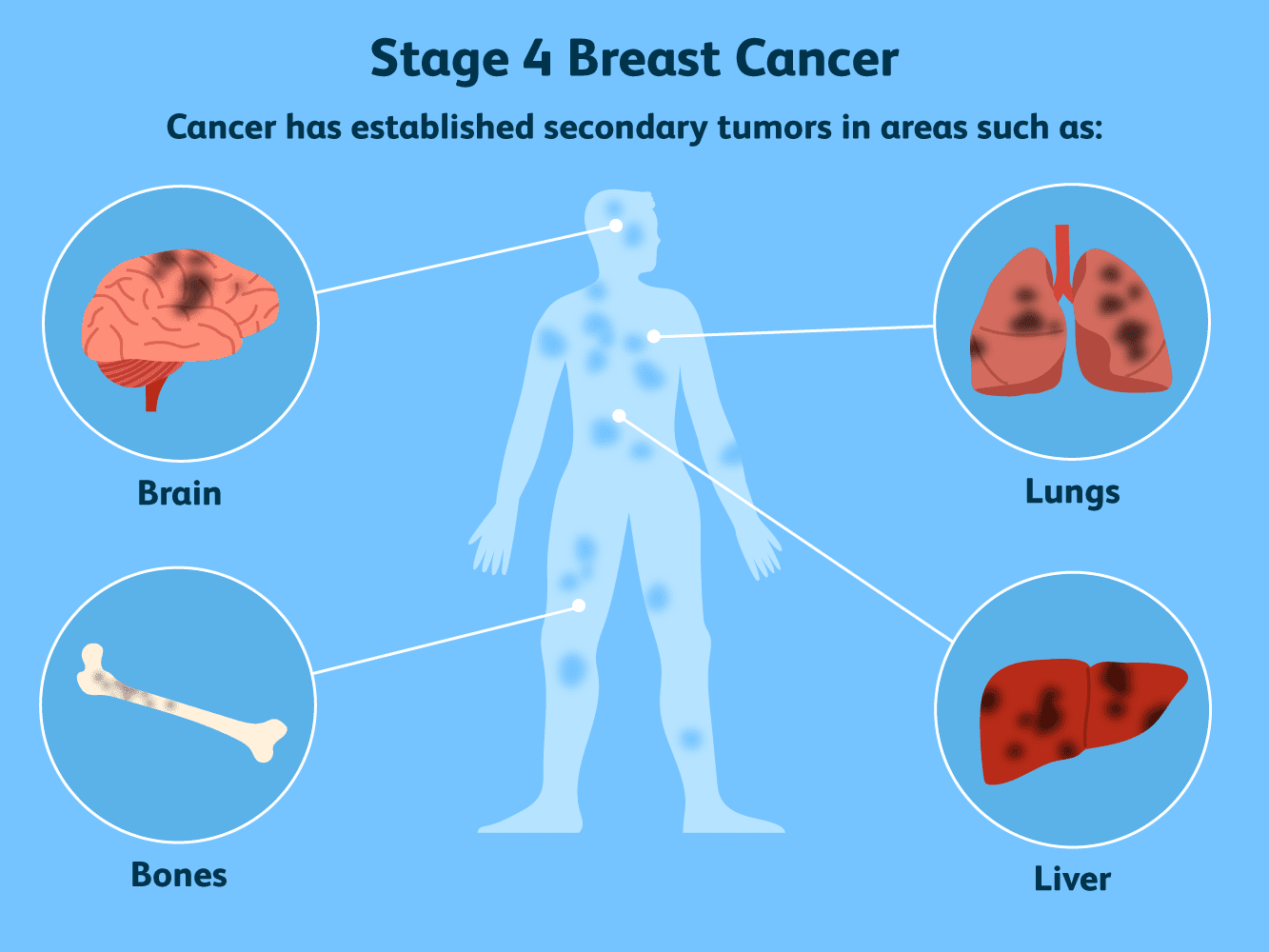
Stage IV (Metastatic Breast Cancer)
Tumor has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes to other organs.
Treatment is usually drug therapy.
Recurrent Breast Cancer
When cancer comes back after primary treatment.
Can happen at the same site or lymph nodes or a different part of the body.